Undergraduate Academic Programs
Browse a complete list of undergraduate academic programs offered by King's College here.
-
Accounting
Program types offered: B.S.
Students selecting an accounting major will earn a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the William G. McGowan School of Business in Wilkes-Barre, Pa. from the Kearney & Company Department of Accounting. A minor in accounting is also available.
Our accounting students learn the skills necessary for success in a dynamic global business environment. We offer a core curriculum, business foundation, and accounting courses that emphasize an awareness of personal values, character development, and critical liberal arts skills such as communication, analytical thinking, team building, and strategic planning.

-
Athletic Training
Program types offered: B.S. / M.S., M.S.
Playing for a professional sports team tops the list of many dream jobs, though opportunities are highly competitive. Many turn their passion for the game into a career as an athletic trainer, helping to improve sports performance by preventing and treating injuries.
Athletic trainers (ATs) are healthcare professionals dedicated to preventing, diagnosing, and treating various medical conditions, particularly those affecting physical performance. They collaborate with physicians and other healthcare providers to optimize the activity of patients and clients. Key qualities of effective athletic trainers include critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, communication skills, and a patient-first approach to care.

-
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Program types offered: B.S.
Have you ever wondered how a scientist discovers drug treatments for cancer? Or perhaps you question why some antibiotics work better than others for certain infections. Have you ever thought about how chemistry can be used by living things? Do you enjoy biology and chemistry and can't decide between the two? Perhaps you are curious about genetics, disease, medicine and how the human body works down to a single molecule in a human cell. The answers to these questions- and many more- can be found in biochemistry and molecular biology.
Biochemistry and molecular biology is an interdisciplinary field of study that combines the knowledge of chemistry with application to living systems. If you enjoy asking questions about how living systems work on a molecular level, or if you are interested in applying chemistry knowledge to solving problems in living systems, then you should consider a biochemistry and molecular biology (BMB) major.
-
Biology
Program types offered: B.S.
Have you ever wondered about the complex living world around us? If you find yourself inspired by the intricate web of life at the cellular level or the grand ecosystems that shape our planet, a bachelor’s degree in biology might be right for you.
At King’s College, our biology program explores the fundamental principles that underlie living organisms, preparing students for a journey that spans from the microscopic structures within cells to the intricate interactions of entire bionetworks.As a biology major, you'll embark on an exploration of the natural world. Whether you aspire to be a research scientist uncovering the mysteries of DNA or a field biologist studying the delicate balance of nature, our program equips you with the knowledge and skills needed to make a profound impact in research, medicine, or education. Many of our students even go on to the health sciences where they apply their understanding of living organisms to help patients in need. Others move on to graduate school or research careers and make contributions as members of the scientific community.
Located in the heart of Wilkes-Barre, Pa., King's College's biology program offers curious minds an opportunity to unravel the complexities of the living world and provides a gateway to diverse career offerings ranging from medical research to environmental conservation.

-
Management – Business Administration
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
Students selecting a major in Management will be awarded a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the William G. McGowan School of Business. A minor in Management is also available as a part of the William G. McGowan School of Business program of study.
The Management major at King's College provides an extensive general background in business; the major requirements emphasize the fundamental principles of business management along with the entrepreneurial and global aspects of business required of a business professional. The management major is provided with a thorough foundation in the fields of accounting, economics, computer systems, law and the quantitative aspects of business. Management majors can choose from a concentration in Business Administration, Entrepreneurship, Healthcare Management, Human Resources Management, International Business Management, or Sports Management. Utilizing the elective courses a student can achieve a double concentration, double major or minor from the other majors in the McGowan School of Business or the College of Arts and Sciences.

-
Chemistry
Program types offered: B.S.
Are you curious about the elements that make up our world? Do you feel at home in a laboratory, learning how even the smallest reactions can change our bodies and the environment around us? If so, earning an undergraduate chemistry degree at King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., could be your gateway to a future of scientific discovery and innovation.
Whether you're captivated by molecular structures or excited by the vast applications of chemistry across various industries, our curriculum is designed to inspire and challenge you. With hands-on laboratory experience and guidance from expert faculty, you'll be well-prepared for advanced studies and diverse career opportunities.

-
Clinical Lab Science and Medical Technology
Program types offered: B.S.
The Bachelor of Science in Clinical Laboratory Science /Medical Technology degree program is designed to train and qualify students as Clinical Laboratory Scientists/Medical Technologists for hospital or clinical laboratories. This program meets the Clinical Laboratory Science requirements of the National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Sciences (NAACLS).
-
Communications
Program types offered: B.A.
A communications degree offers students the opportunity to gain a broad understanding of the media’s role in society, along with a highly specialized and personalized concentration in their area of professional interest – Broadcast and Social Media, Journalism, Video Game Design, or Visual and Brand Communications. See what students have to say about the program. More details are available here, too!
Students are taught how to understand and critically evaluate the past, present and future of mass communications so that they are prepared to excel within its ever-changing structure and to produce changes within it. The program provides a mix of hands-on and theoretical courses in order to provide students with a well-rounded education. Students will thereby develop a foundation in both the creation of media and comprehension of the effects and significance of media products that they create and consume.

-
Computer and Information Systems
Program types offered: B.S.
Are you a problem-solver with an affinity for technology? Do you have an analytical mind and a knack for understanding complex systems? If so, a computers and information systems (CIS) degree from King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., might be the perfect fit for you.
In our CIS program, you will gain hands-on experience in areas such as software development, database management, networking, cybersecurity, and data analytics. You will learn how to develop and implement computer systems that help organizations operate efficiently and securely. Our curriculum combines technical skills with critical thinking, allowing you to tackle complex problems in real-world scenarios.
At King’s College, we empower our students to take charge of their career paths, achieve their goals, and prepare for a successful future.

-
Computer Science
Program types offered: B.S.
Computer science is the study of computer systems and their rapidly expanding role in households, businesses, and government agencies around the world. As computers have expanded into all aspects of daily life, computer scientists are needed to improve user interfaces, digital networks, data storage, cybersecurity, and web design. We focus on understanding the diverse properties of computer systems used in medical diagnosis, scientific visualization, biological simulation, artificial intelligence, and engineering design.
Earning a computer science degree is a worthwhile investment for professional growth and future employment. According to the U.S. Department of Labor, the median annual salary for this field is $97,430 and related jobs are projected to grow 15% from 2021 to 2031, which is much faster than most other occupations.
-
Criminal Justice
Program types offered: B.A.
The criminal justice system protects the rights of the victim and the accused by ensuring justice is served for both. If you dream of being a detective, security specialist, or prosecutor, this may be the major for you.
Criminal justice is a captivating field that analyzes how criminal offenders are processed by federal, state, and local agencies. It examines law enforcement officers, courts, and corrections.
Students pursue a criminal justice degree for many reasons, including a desire to help their community and contribute to a safer society. Aspiring professionals in this field often feel a strong sense of social responsibility and seek to uphold justice, protect the vulnerable, and promote fairness within the criminal justice system.
At King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., we equip students with a deep understanding of the criminal justice system and its impact on society so they can solve crimes, succeed in a courtroom, or pursue any number of rewarding careers that contribute to the public good.
-
Economics
Program types offered: B.A.
Have you ever pondered the intricate web of decisions that shape our society and the global economy? If you are intrigued by the complex dynamics that govern markets across the world, a B.A. in Economics at King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., can be your gateway to a fulfilling and impactful career.
Understanding the underlying economic principles is essential in a rapidly evolving world characterized by technological advancements, global trade, and political shifts. Economics considers the impact of small and large resource decisions on the individual, society, and the natural world. It provides the analytical tools to dissect and craft practical solutions to today's pressing issues.

-
Education
Program types offered: B.A.
Do you remember that special teacher who made a difference in your life? Perhaps it was a first-grade science teacher who sparked your love of biology. Or a high school English teacher who recognized your creative potential and inspired you to hone your writing skills.
Educators shape lives, ignite passions, and instill knowledge that lasts a lifetime. At King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., we want to help you become that transformative influence in a student’s life.
We offer a diverse selection of education degree programs, whether you’re seeking certification in elementary, middle, or secondary education. Regardless of which certification you choose, our coursework ensures you acquire the skills and knowledge needed to excel in your chosen field.
We welcome you to join our community of educators, learners, and visionaries. Together we can shape the future by nurturing young minds and empowering the next generation!

-
Engineering – 3+2 Accelerated
Program types offered: B.S. / B.S.
King’s College offers 3+2 Dual Degree Engineering Programs in collaboration with the University of Notre Dame and Washington University in St. Louis. In these programs students study for three years at King’s College taking mathematics, science, pre-engineering and liberal arts courses, and then transfer to Notre Dame or Washington University for two years to complete engineering courses in their chosen fields. Upon successful completion of the program, students receive both a B.S. from King’s College (in Physics, Chemistry, Environmental and Ecological Sciences or Computer Science) and a B.S. in Engineering from Notre Dame (in Aerospace, Chemical, Civil, Computer, Electrical, Environmental or Mechanical Engineering) or Washington University (in Biomedical, Chemical, Computer, Electrical, Environmental, Mechanical or Systems Engineering).
The 3+2 Engineering program at King’s takes an interdisciplinary approach to exposing students to the transferable skills of liberal learning valued in a King’s College education. The knowledge, skills, and dispositions students acquire by virtue of the Core liberal arts curriculum at King’s will enhance their ability to be successful contributors within their chosen engineering field. During the three years at King’s, students take a variety of liberal arts courses that develop skills in written and oral communication, moral reasoning, and critical thinking. Employers value the liberal arts/engineering combination since students possess not only technical skills, but also the ability to write proposals, make presentations, and broadly understand engineering systems and the role of technology in our changing society.
-
Engineering – Civil
Program types offered: B.S.
A civil engineering degree from King's will set you up for a lucrative and rewarding career designing all kinds of structures that help people, including bridges, dams, airports, harbors, and skyscrapers.
The first building block for that career is a strong educational foundation. With a civil engineering bachelor's degree from King's, our graduates enter the workforce with real-world engineering experience and a strong desire to use their skills in the service of others.

-
Engineering – Mechanical
Program types offered: B.S.
You'll use creative design throughout your time at King's, from your first semester all the way to your final capstone project when you build a machine for an actual client. You could come up with a device that factory workers use to move heavy metals, a machine that controls flow for manufacturing particles, or even build a robot that uses ultrasound to navigate autonomously.
This experience is possible because our faculty work closely with students in small classes. We'll help you match your talents and passions with exciting opportunities in the real world. Our mechanical engineering curriculum is driven by the insights of our partners in industry, who know the importance of creativity, practical thinking, and professional skills like teamwork and communication.
-
English – Literature
Program types offered: B.A.
Are you drawn to stories and the power of words? Do you enjoy digging deeper to find the hidden meanings in texts? If so, an English Literature degree from King's College may be the perfect fit for you. Choosing to major in English prepares you for graduate study in literature, a future in creative writing, and beyond. A degree in English Literature is your gateway to rewarding careers in various fields, including publishing, education, law, marketing, journalism, or public relations.
The English Department offers students a wide range of writing and literature courses, fostering creativity and critical thinking. The department also serves as dedicated advisors to all our majors and minors, both in their academic pursuits at King’s and in their lives beyond college.
Located in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, King's College is dedicated to fostering a community of curious minds passionate about delving deep into the literary world.

-
English – Professional Writing
Program types offered: B.A.
As one of the largest departments on campus, the English Department provides students with a variety of literature and writing courses and serves as dedicated, student-centered advisors to all our majors and minors, both in their academic pursuits while here at King’s and in their lives beyond college.
Students in English can choose among three majors: the Bachelor of Arts in English, the Bachelor of Arts in English with Secondary Education Certification, or the Bachelor of Arts in Professional Writing. The Bachelor of Arts in English emphasizes the analysis of literary and cultural texts in a range of historical and aesthetic contexts. The Secondary Education degree emphasizes the same knowledge and skills, but with an added component of classes focused on education and pedagogy. The Bachelor of Arts in Professional Writing includes the study of the art of writing (both professionals and creative, rhetorical theory (including visual and digital rhetoric), the practicalities of day-to-day workplace writing, and an introduction to some of the software and technologies on which professional writers (and their employers) depend.

-
Management – Entrepreneurship
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
Students selecting a major in Management will be awarded a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the William G. McGowan School of Business. A minor in Management is also available as a part of the William G. McGowan School of Business program of study.
The Management major at King's College provides an extensive general background in business; the major requirements emphasize the fundamental principles of business management along with the entrepreneurial and global aspects of business required of a business professional. The management major is provided with a thorough foundation in the fields of accounting, economics, computer systems, law and the quantitative aspects of business. Management majors can choose from a concentration in Business Administration, Entrepreneurship, Healthcare Management, Human Resources Management, International Business Management, or Sports Management. Utilizing the elective courses a student can achieve a double concentration, double major or minor from the other majors in the McGowan School of Business or the College of Arts and Sciences.
-
Environmental Chemistry
Program types offered: B.S.
Do you ever wonder how the smallest environmental changes can affect the food we eat, water we drink, and air we breathe? If so, an environmental chemistry degree at King's College could be your gateway to a meaningful career addressing some of the planet's most pressing challenges.
Choosing an environmental chemistry degree means diving deep into the chemical processes that shape our environment, from pollution and climate change to everyday human activities. Graduates from our program are well-prepared to contribute to the preservation and protection of our planet.
Job prospects for those with an environmental chemistry degree are promising. Environmental chemists can find rewarding careers in consulting, government agencies, research institutions, and more. As the demand for skilled professionals in this field grows, so does the value of this degree.
At King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., our environmental chemistry program offers a robust curriculum covering essential topics like toxicology, environmental analysis, and sustainable practices. You'll benefit from state-of-the-art laboratories and expert faculty who are passionate about guiding you through your academic journey.
A unique feature of our environmental chemistry program is our students have the potential to graduate with an American Chemical Society (ACS)-certified degree, which is a major asset in today’s job market.
Explore our environmental chemistry degree program and take the first step toward an exciting, lucrative, and fulfilling career.

-
Environmental and Ecological Science
Program types offered: B.S.
Are you intrigued by the natural world and passionate about addressing the pressing environmental challenges of our time? Do you enjoy working with plants, animals, and their habitats? If you find yourself drawn to understanding and solving ecological issues, then an environmental science degree may be the perfect path your you!
At King’s College, our Environmental and Ecological Sciences Degree (B.S.) is tailored for those eager to learn the complexities of the environment and play an active role in its stewardship.
Environmental science is a dynamic and interdisciplinary field focused on organisms and their environments. Our environmental science degree program combines a broad interdisciplinary science and social science background within a flexible curriculum. Located in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, King’s College provides a holistic educational experience that combines top-tier academics with practical, real-world applications.

-
Environmental and Sustainability Studies
Program types offered: B.A.
Have you ever wondered how your actions impact the world around you? In an era where climate change and sustainability are not just buzzwords but eminent concerns, understanding our environment has never been more crucial. At King's College, we don't just teach you about environmental issues: we immerse you in the solutions.
If you're passionate about making a tangible difference in the world, a degree in environmental and sustainability studies may be right for you.
-
Exercise Science
Program types offered: B.S.
A Bachelor of Science (B.S.) in Exercise Science is focused on the study of physical activity and its impact on health, wellness, and athletic performance. This multidisciplinary field combines biology, physiology, psychology, and nutrition to understand how exercise affects the human body and mind.
Students learn to design effective exercise programs for a wide range of populations, including athletes, individuals with chronic diseases, and those seeking to improve their overall health and fitness. Graduates with a B.S. in Exercise Science are prepared for careers in fitness and wellness coaching, strength and conditioning, rehabilitation, and health education. They may also pursue further education in physical therapy, occupational therapy, exercise physiology, medicine, and other health-related professional programs.
King’s College's Exercise Science program in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., is one of the first in the United States, and the first undergraduate program in Pennsylvania, to receive accreditation from both the Council on Accreditation of Strength and Conditioning Education (CASCE) and the National Strength and Conditioning Association (NSCA).
-
Finance
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
While earning your finance degree, King's provides an extensive general background in business; the major requirements emphasize the fundamental principles of business management along with the entrepreneurial and global aspects of business required of a business professional. This encompasses a thorough foundation in the fields of accounting, economics, computer systems, finance, law and the quantitative aspects of business. Finance majors can choose from a concentration in Business Administration, Entrepreneurship, Healthcare Management, Human Resources Management, International Business Management, or Sports Management. Utilizing the elective courses a student can achieve a double concentration, double major or minor from the other majors in the McGowan School of Business or the College of Arts and Sciences.

-
French
Program types offered: B.A.
The Department of Foreign Languages offers courses designed to help the student develop skills in speaking, writing, reading, and understanding a foreign language. In doing so, this may enhance the student’s employment opportunities in a variety of ways, in addition to contributing to the student’s broad humanistic education.
The main objectives of the French major are to increase the student’s communication skills in French and enhance their understanding and appreciation for the French culture. This instruction and preparation provides the necessary background needed for careers in foreign language teaching, bilingual education, teaching English as a second language, and areas of graduate study. Pursuing a French major, in conjunction with another specialization, can not only aid the student when traveling, but also open up career opportunities fields such as government, international business/commerce, accounting, law, and communications.

-
General Science
Program types offered: B.S.
A major program in General Science is available to students whose goals and interests require a diversity of exposure to science disciplines and flexibility in selection of science courses. The major in General Science is appropriate for students who are preparing for careers in the health professions (Pre-Medical, Pre-Dental, Pre-Veterinary, etc.), for those who wish to enter graduate school programs at the Masters or Doctoral degree levels, for those students who wish to attain Teacher Certification, and those preparing for employment in a variety of science or science-related career areas.
The major sequence course requirements for the General Science Major provide a breadth of exposure to the science disciplines; the choices available for minor concentration provide diversity and flexibility so that a student can readily obtain specific preparation needed for individual postgraduate plans.
-
Management – Healthcare Management
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
Students selecting a major in Management will be awarded a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the William G. McGowan School of Business. A minor in Management is also available as a part of the William G. McGowan School of Business program of study.
The Management major at King's College provides an extensive general background in business; the major requirements emphasize the fundamental principles of business management along with the entrepreneurial and global aspects of business required of a business professional. The management major is provided with a thorough foundation in the fields of accounting, economics, computer systems, law and the quantitative aspects of business. Management majors can choose from a concentration in Business Administration, Entrepreneurship, Healthcare Management, Human Resources Management, International Business Management, or Sports Management. Utilizing the elective courses a student can achieve a double concentration, double major or minor from the other majors in the McGowan School of Business or the College of Arts and Sciences.
-
History
Program types offered: B.A.
History stands at the crossroads of the liberal arts. It belongs fully to two great academic families: Social Sciences and the Humanities. Studying history, reading, writing and arguing about history, questioning the past and our relationship to it, are fundamental questions that frame our understandings of ourselves as individuals and the societies we inhabit. History tells us who we are. Equally importantly, history is about sources and evidence—about how we sort through voices of the past and present, in order to understand more fully the society, culture, politics and economy of the world around us. King’s History students will emerge better able to understand the forces which have shaped our world, to address current problems based on historical thinking, and to communicate these understandings effectively.

-
Management – Human Resources Management
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
Students selecting a major in Management will be awarded a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the William G. McGowan School of Business. A minor in Management is also available as a part of the William G. McGowan School of Business program of study.
The Management major at King's College provides an extensive general background in business; the major requirements emphasize the fundamental principles of business management along with the entrepreneurial and global aspects of business required of a business professional. The management major is provided with a thorough foundation in the fields of accounting, economics, computer systems, law and the quantitative aspects of business. Management majors can choose from a concentration in Business Administration, Entrepreneurship, Healthcare Management, Human Resources Management, International Business Management, or Sports Management. Utilizing the elective courses a student can achieve a double concentration, double major or minor from the other majors in the McGowan School of Business or the College of Arts and Sciences.
-
Management – International Business Management
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
Students selecting a major in Management will be awarded a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the William G. McGowan School of Business. A minor in Management is also available as a part of the William G. McGowan School of Business program of study.
The Management major at King's College provides an extensive general background in business; the major requirements emphasize the fundamental principles of business management along with the entrepreneurial and global aspects of business required of a business professional. The management major is provided with a thorough foundation in the fields of accounting, economics, computer systems, law and the quantitative aspects of business. Management majors can choose from a concentration in Business Administration, Entrepreneurship, Healthcare Management, Human Resources Management, International Business Management, or Sports Management. Utilizing the elective courses a student can achieve a double concentration, double major or minor from the other majors in the McGowan School of Business or the College of Arts and Sciences.
-
International Relations and Strategy
Program types offered: B.A.
The challenges facing the world today are not bound by traditional borders. Technological innovation, climate change, and war always impact multiple nations at a time. Likewise, a major program that is not bound by traditional disciplinary boundaries offers the best approach to tackling these challenges.
The Bachelor of Arts in International Relations and Strategy at King’s College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., integrates political science, history, economics, geography, and language courses into the study of contemporary global questions.
-
Law Degree (J.D.)
Program types offered: Juris Doctor
Are you interested in pursuing a legal degree? If so, the law program at King's College, in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., is your gateway to success. Explore the enriching opportunities that await you here and take the first step towards becoming an attorney.
We equip you with critical thinking, analytical skills, and the ethical foundation necessary for a successful legal career. With a curriculum tailored to a smooth transition into law school, you'll gain invaluable insights and knowledge that set you apart from the competition. We pride ourselves on fostering a supportive and engaging learning environment, ensuring you are well-prepared for the challenges ahead.
Our law program features accelerated tracks with Duquesne University and Villanova University. As one of our law students, you can complete your undergraduate requirements at King’s College before transferring to a partner law school to complete your J.D. Please review these options below.
 Villanova University
Villanova University -
Marketing
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
Students selecting a major in marketing will earn a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (B.S.B.A.) degree under the program of study offered by the King's College William G. McGowan School of Business in Wilkes-Barre, Pa. A minor in marketing is also available.
The Bachelor of Science in Business Administration degree with a major in marketing is designed to foster a detailed understanding of the marketing field and its role in business.

-
Mathematics
Program types offered: B.A.
The aim of the Mathematics Department is to provide mathematics degree students with a sound background in both pure and applied Mathematics, while inculcating a respect for objective reasoning, clear ideas, and precise expression (elements which truly characterize a liberal arts education). Our goal is to make students sophisticated in the way they think and in the way they approach problems. This heightened sophistication should extend beyond the boundaries of mathematics into other areas.
The Mathematics Department provides a thorough undergraduate training in mathematics for those desiring mathematical careers in education, research, industry, and government, and courses for those who wish to follow a limited programming mathematics.
-
Neuroscience
Program types offered: B.S.
The Neuroscience major at King’s College emphasizes a collaborative and interdisciplinary approach to understanding the complex neural mechanisms involved in the control of human or animal behavior. The major provides students with a broadly based yet integrated education focused on the relationship between behavior and biology at multiple levels.
The Neuroscience major requires courses in introductory biology, chemistry, psychology, organic chemistry, statistics, and a survey of neuroscience. Students then select a number of more advanced psychology and biology courses as electives, allowing them to focus on the area of neuroscience that is of most interest. Students receive laboratory experience to help them develop scientific process skills (i.e., critical thinking, and writing). All students engage in original research under the supervision of a faculty member. Students completing the major will have an interdisciplinary scientific background from which to pursue their individual interests in the neurosciences.
-
Nursing
Program types offered: B.S.
For individuals who are inspired by helping others, there are few career paths more rewarding than nursing. Nurses are at the front lines of critical medical care, often having the first and most frequent interactions with patients in need. And as healthcare challenges across the country expand, so do employment opportunities for professionals in this field.
A career in nursing opens the door to opportunities in Adult Health, Pediatrics, Obstetrics, Psychiatry, and more. Key responsibilities include:
- Promoting wellness and disease prevention
- Providing education on chronic disease management
- Coordinating regenerative and restorative care
- Administering hospice and palliative care

-
Occupational Therapy
Program types offered: B.S. / O.T.D., O.T.D., Hybrid
Human beings live and learn through meaningful occupations that evolve across our lifespan and are essential to our well-being and quality of life. Daily occupations like bathing, eating, working, traveling, and socializing are just some of the activities that shape our personal development and nurture our physical and mental health.
However, injuries, chronic health issues, and disabilities can prevent us from enjoying even the most basic activities that many take for granted every day. Helping people overcome those limitations lies at the very heart of the occupational therapy profession.
Whether you are a first-time student coming out of high school, a college graduate, or a licensed occupational therapist, we welcome you to explore the Doctor of Occupational Therapy (OTD) programs at King’s College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa.

-
Philosophy
Program types offered: B.A.
Philosophy (Greek for “love of wisdom”) addresses deep and fundamental questions of human existence: Is there a God? What is the meaning of life? What is ultimately real? What is mind, and how does it relate to the physical world? How should one make moral decisions? What is a just society? As the rigorous, systematic study of such big questions, philosophy is central to the mission of King’s College, which seeks to produce broadly educated men and women who possess a clear moral compass, are capable of articulate and critical reflection on the fundamental problems of the human condition, and are informed and reflective citizens.

-
Physician Assistant
Program types offered: B.S.M.S. / M.S.P.A.S.
Do you have a passion for helping people with the latest advancements in medical care? Are you prepared to enter a challenging, rewarding, and high-paying profession with countless employment opportunities?
If so, our physician assistant (PA) degree offers multiple advantages that will help you secure a promising future in medicine. Our faculty and clinical preceptors include physician assistants, physicians, and other health care professionals who are eager to guide you throughout your academic journey, whether you are first time student or a professional looking to advance your career.

-
Physics
Program types offered: B.S.
Physics is the broadest of the natural sciences, and more than any other, seeks to explain the nature of the universe. Physics is the discipline that investigates the inner workings of the world in which we live and seeks to understand the properties and interactions of atoms, nuclei and the fundamental particles of the Universe. It deals with the forces that govern the history and the future of the Universe, from the time of its birth to its ultimate fate. And, on a more practical scale, physics helps us understand the workings of the human body, the properties of engineering materials, and the most efficient uses of energy. Whatever the question, it is likely that physics holds the answer.
King’s equips physics graduates with key attributes desired by employers: the ability to analyze and solve complicated problems, experience with computers and an understanding of modern technology, an ability to place physics in a global and cultural context, and the ability to effectively communicate essential knowledge in oral, written, and quantitative forms. With this background, students with a degree in physics can find jobs in the private sector including jobs related to engineering, computer or information systems, in the government sector at national research labs, in the military, in the finance and banking industry, in the secondary education system, and in professional programs like medical school or law school.
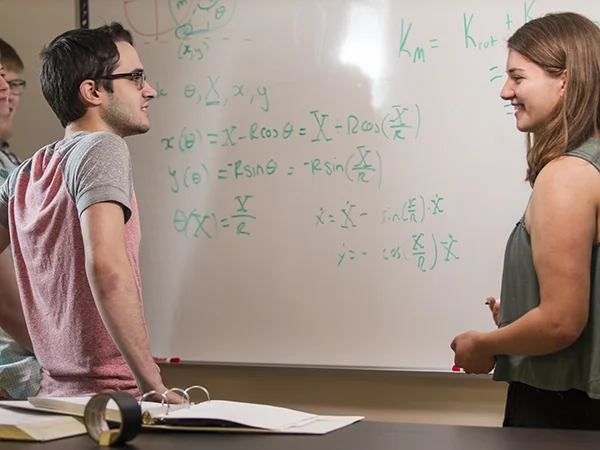
-
Political Science
Program types offered: B.A.
Embarking on the journey to earn a political science degree at King's College unlocks a deeper understanding of government, power dynamics, policy, and diplomacy. Our program equips students with critical thinking and analytical skills essential for navigating the complexities of the political landscape. With a blend of theoretical foundations and practical applications, our curriculum prepares graduates for diverse political science careers in public service, law, and beyond.
Discover how a political science degree from King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., can shape your future.

-
Pre-Health
Program types offered: B.S.
The Pre-health Professions Program at King’s College provides all of the resources you need to successfully enter a graduate program in Medicine, Dentistry, Veterinary Medicine, Chiropractic Medicine, Podiatry, Optometry, Nursing, Physical Therapy, Pharmacy, Physician Assistant, Athletic Training, and other clinical health professions. Similar to a pre-med major program, we offer a wealth of individual and group opportunities for our students as they progress from freshman year through admittance into their professional program.
King’s College offers 5-year BS/MS Programs for students wishing to pursue Physician Assistant or Athletic Training careers. These programs are composed of a pre-professional and professional phase. King's also offers a competitive undergraduate Nursing program including an RN to Bachelor of Science Degree and the Dual Degrees in Nursing (DDN) program. We encourage you to learn more about these exciting programs!
The Exercise Science Occupational Therapy Track (3+3 OTD track) BS/OTD program requires six years of academic studies, including six months of clinical fieldwork and a 14-week doctoral capstone experience. This accelerated degree program leads to an entry-level Clinical Doctorate after graduating with a Bachelor of Science in Exercise Science with a Minor in Neuroscience.

-
Psychology
Program types offered: B.S.
Do you find yourself thinking about why people do what they do? Are you curious about the experiences, feelings, and thoughts that influence how we perceive the world? Your interest could indicate a more than casual curiosity into what makes our minds tick.
Knowledge and appreciation of human interaction are essential for success in our rapidly expanding and diverse society. A psychology degree offers insight into understanding the thoughts, emotions, and actions that shape who we are, and explores the dynamics of human interaction.
As a psychology major at King's College in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., you will gain insights into the various theories that form the foundation of psychology and develop practical skills that enable you to comprehend, analyze, and interpret human interactions. Whether you're leaning towards clinical practice, research, government, or business our distinguished B.S. and B.A. psychology degree programs will provide a solid foundation to realize your ambitions.

-
Social Work
Program types offered: B.A.
Social workers connect vulnerable and disadvantaged people with essential welfare systems, assistance programs, and resources.
Their help reaches individuals, families, and community groups struggling with disabilities, mental health concerns, addiction, violence, or trauma. Social workers also help marginalized youth, veterans, the elderly, incarcerated individuals, and unhoused, immigrant, or refugee communities.
With a social work degree, you’ll advance human rights and social, economic, and environmental justice. You’ll identify diverse community groups and how their identities impact social experiences. You’ll also assess and engage with individuals, families, groups, organizations, and communities while developing policy and conducting research.
-
Sociology
Program types offered: B.A.
Sociology is the scientific study of human interaction and society. Understanding and predicting how social groups -- ranging from workplace teams to entire societies -- function and change is the goal of the discipline. It includes the study of institutions such as family, work/occupations, education, religion, military, welfare, and social work. Also prominent in Sociology is the study of the problems facing society such as crime, poverty, juvenile delinquency, terrorism, aging, and minority/majority group relations. It is unique among the social sciences because it is not limited in focus to a single institution or level of analysis, but emphasizes the relations among all parts of society.

-
Spanish
Program types offered: B.A.
The Department of Foreign Languages offers courses designed to help the student develop skills in speaking, writing, reading, and understanding a foreign language. In doing so, this may enhance the student’s employment opportunities in a variety of ways, in addition to contributing to the student’s broad humanistic education.
Knowledge of Spanish, especially in combination with another field of study, provides countless opportunities for engaging and rewarding careers within the global economy. It may also create a unique opportunity for those studying education, as the demand for bilingual educators and English instruction increases. Spanish is a very global language, spoken as the first language in Spain, Argentina, Mexico, Costa Rica, and the Dominican Republic. Many United States residents also speak Spanish as their native language.
The main objectives of the Spanish major program are to strengthen the student’s understanding and fluency in the language while teaching them about the culture behind it.

-
Management – Sports Management
Program types offered: B.S.B.A.
The new Sports Management concentration is designed for students who seek to apply their business skills to the dynamic industry of sports and recreation. Earning a sports-management-focused degree will position graduates to navigate the sports marketing and media environment; understand labor and sports law; manage budgets and complex financial issues; manage teams, events, and projects; and leverage business technology for problem solving and data-informed decision making.
The global sports industry generates over $400 billion annually, and the number and type of associated career opportunities is growing faster than average (10% from 2016 to 2026). Graduates can expect to work in facility and event management, marketing and promotion, sports communication, sales, sports tourism, or amateur and professional sport management organizations, among others, with average salaries ranging from $41,000 to $208,000.
At King’s, students will have regional access to practicum and internship opportunities at high-profile organizations like the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins (AHL Pittsburgh Penguins) and the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders (Triple-A Yankees).

-
Theatre
Program types offered: B.A.
Theatre is a vibrant study of humanity, a mirror to society, and a pathway to self-discovery. If you find yourself drawn to the limelight, intrigued by the art of storytelling, or passionate about affecting change through performance, then a theatre major at King’s College is your spotlight.
Theatre is an ancient tradition, a contemporary craft, and a future-facing career. Our theatre program equips you with highly transferrable skills such as public speaking, collaboration, problem-solving, and adaptability—which help you to grow on and off the stage.
At King’s College, located in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, we believe in the power of theatre. A B.A. in theatre is your gateway to understanding diverse narratives and a platform you to develop your unique voice.Through hands-on experience, you’ll build confidence, critical thinking, and a strong professional presence, enhancing your marketability in any field you choose.

-
Theology
Program types offered: B.A.
Why study theology? You might want to explore your faith or your questions about the meaning of life. Perhaps you wonder about God, human dignity, justice, or how to live a good life. Often described as “faith-seeking understanding,” theology invites you to engage your mind and heart in your studies. As you gain skills in theological reflection, you will explore the sources, traditions, and challenging questions related to religious belief.
Students pursuing majors or minors in theology at King’s College enjoy a broad offering of courses in theological reflection, individualized attention from dedicated theological faculty, and the company and support of a caring community. As a small, liberal arts, Catholic college, in Wilkes-Barre, Pa., King’s promotes academic excellence, transformative study, interfaith cooperation, and service to the common good. Come and discover your future career or vocation with us!
